Currently, about half of all conventionally printed fabrics are printed using pigment inks, the majority of this is made up from analogue screen printing, where long runs are required for efficiency. Digital printing direct to fabric using Pigment ink has gained in popularity over recent years, this can be more efficient as you can print in short runs on demand.
Fabric printing can also be broken into two distinct categories, Direct To Garment (DTG), and Direct To Fabric (DTF) printing. While DTG printing mostly utilises pigment ink, the focus of this article will be DTF digital printing.
Pigment ink for digital printing consists of finely ground pigment powder combined with a binder and suspended in water. Printing direct to the fabric, followed by heat setting to evaporate the water, the binders adhere the pigments to the fibres of the textile.
Pigment inks use a basic set of chemicals and pigments that are fairly cost-effective to produce, combined with the relatively simple production process the overall cost to produce a finished print are significantly lower compared to other ink sets.
Historically the main hurdle digitally printed Pigment inks have faced have been the solid content in the inks, which have caused challenges for print heads at high-speed printing. Advances in pigment ink manufacturing have seen those challenges overcome.
Many competing ink sets are linked to printing onto certain types of fabrics, whereas pigment ink by its nature does not distinguish between various fibres. It does not rely on a chemical reaction to bond the pigment to the fibre but rather uses a binder.
You can print pigment ink onto many substrates including natural fibres (e.g. cotton, linen, bamboo, silk, viscose) as well as synthetic fibres (e.g. polyester, nylon). A further significant advantage is that it is also suitable for blended fabrics such as cotton/polyester, which is the most commonly printed fabric globally.
Whilst pigment ink can print on a large variety of fabrics, the final results are greatly enhanced if the textiles are prepared for digital printing with pigment ink (PFDPP). The benefits are increased colour brilliance and wash fastness which is crucial for certain applications such as fashion and apparel.
Pigment ink printing is used in all major textile sectors including fashion, apparel and sportswear as well as interior décor/home textiles. To a lesser extent also for soft signage that has been dominated by dye-sublimation.
Pigment inks are usually not chemically reactive and do not have any of the allergens that are found in dye-based ink sets and are therefore preferred for sensitive applications, such as babywear.
As existing print systems are being updated, more textile manufacturers will choose digital inkjet printing systems with pigment ink to replace old analogue technology. The easy process makes this ideal also for companies with less knowledge in that space to access the markets unlocked by this technology. Many start-up businesses choose this technology to cater for the trend towards custom made individual items and print on demand, ideal for more bespoke markets.
Digitally printed Pigment ink offers sustainability, efficiency, versatility, and flexible manufacturing. With digitally printed natural fabrics increasing in demand, this is an area we expect to see significant growth in the coming years.
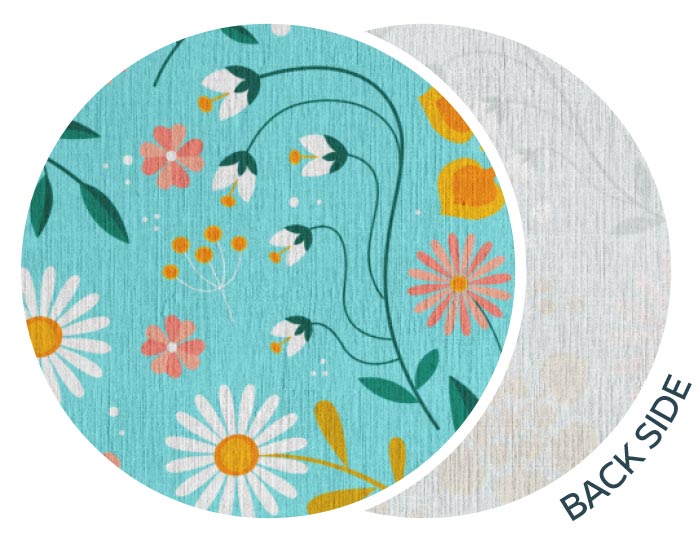
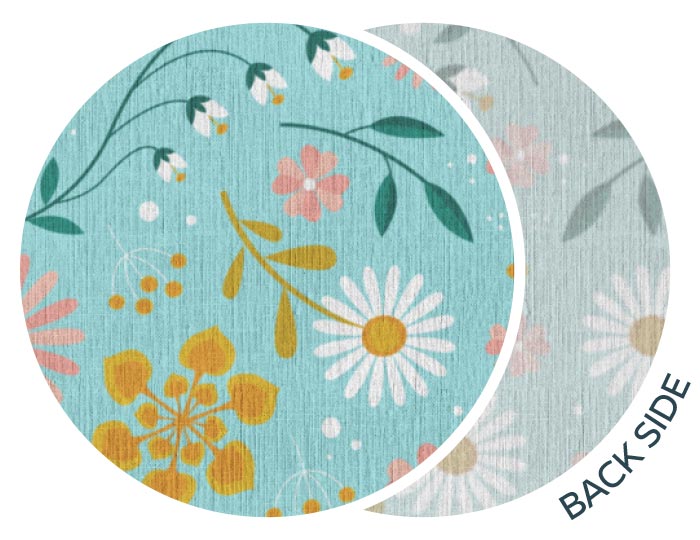
















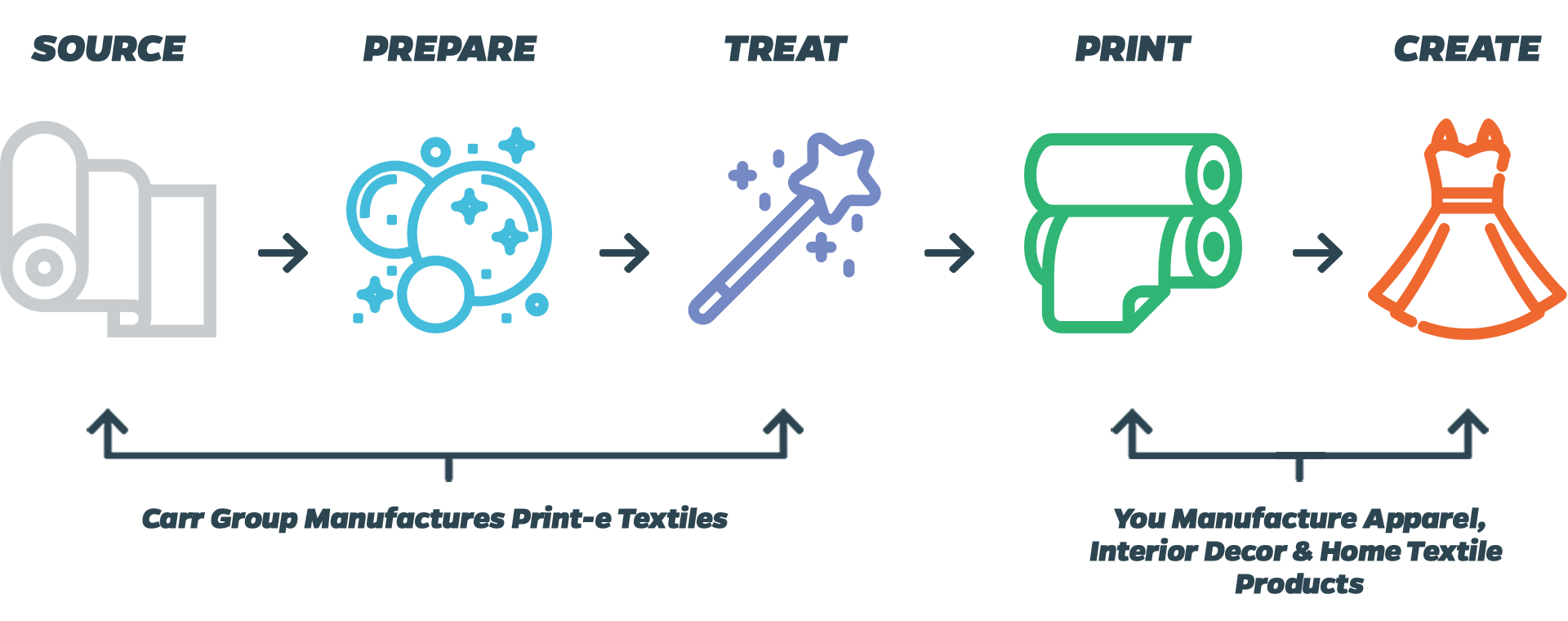 Carr Group sources the highest quality textiles from around the world and prepare them for digital printing. This preparation ensures that the fabric is clean of oils, waxes, sizing agents from the manufacturing process and has no loose fibres on the surface as well as having clean selvedges (edges of the fabric). Further treating a fabric with Britelok typically involves a treatment bath designed for a particular ink type.
Carr Group sources the highest quality textiles from around the world and prepare them for digital printing. This preparation ensures that the fabric is clean of oils, waxes, sizing agents from the manufacturing process and has no loose fibres on the surface as well as having clean selvedges (edges of the fabric). Further treating a fabric with Britelok typically involves a treatment bath designed for a particular ink type.